COSO Framework
UW-Madison is utilizing the COSO Internal Controls Framework as a guideline for establishing its own internal financial controls framework. The COSO Framework provides an established, best-practice set of concepts and components by which to assess control systems. Applying the COSO Framework as a foundational point in this initiative will help UW-Madison more efficiently identify the objectives and requirements needed to define and support excellence in financial stewardship.
The COSO Cube: Internal Controls Framework and Principles
One page for print (PDF)

What is COSO?
The Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). Visit the COSO website.
COSO is an organization that provides thought leadership to executive management and governance entities on critical aspects of organizational governance, business ethics, internal control, enterprise risk management, fraud, and financial reporting. It was formed in 1985 to sponsor the National Commission on Fraudulent Financial Reporting (the Treadway Commision). COSO is supported by the following five organizations:
- The Institute of Management Accountants (IMA)
- The American Accounting Association (AAA)
- The American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA)
- The Institute of Internal Auditors (IIA)
- Financial Executives International (FEI)
COSO has established a common internal control framework against which companies and organizations may assess their control systems. The COSO framework is based on these key concepts:
- Internal control is a process. It is a means to an end, not an end in itself.
- Internal control is affected by people. It's not merely policy, manuals, and forms, but people at every level of an organization.
- Internal control can be expected to provide only reasonable assurance, not absolute assurance, to an entity's management and board.
- Internal control is geared to the achievement of objectives in one or more separate but overlapping categories
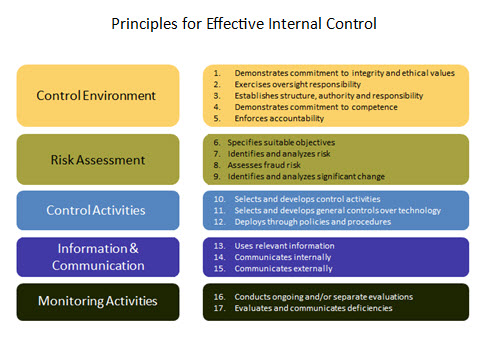
Components of an Internal Control Framework
| Control Environment |
|
| Risk Assessment |
|
| Control Activities |
|
| Information and Communication |
|
Monitoring and Review |
|
